Gemma Scope 2: Illuminating the Black Box of AI
How Amlgo Labs and the Research Community Are Deepening Our Understanding of Language Model Behaviour
The rapid advancement of large language models has brought unprecedented capabilities, yet paradoxically, as these models grow more powerful, they become more opaque. Understanding what happens inside these AI systems remains one of the most pressing challenges in AI safety.
Enter Gemma Scope 2, a groundbreaking open-source toolkit that’s transforming how researchers peer into the inner workings of language models. At Amlgo Labs, we’ve been closely following and contributing to mechanistic interpretability, recognising that transparency isn’t just a technical nicety, it’s fundamental to building trustworthy AI.
The Interpretability Challenge
Modern language models are vast neural networks with billions of parameters. When you input a query, it passes through hundreds of layers before producing output. But what happens in between? What concepts does the model form? How does it reason through problems?
These aren’t academic questions. Without interpretability, we face critical risks: undetectable biases, catastrophic edge case failures, and decisions we can’t audit. For AI deployed in healthcare, finance, or legal systems, this opacity is unacceptable.
What Makes Gemma Scope 2 Different
Gemma Scope 2 employs sparse autoencoders to decompose model activations into interpretable features. The innovation lies in identifying monosemantic features and neural patterns corresponding to specific, human-understandable concepts.
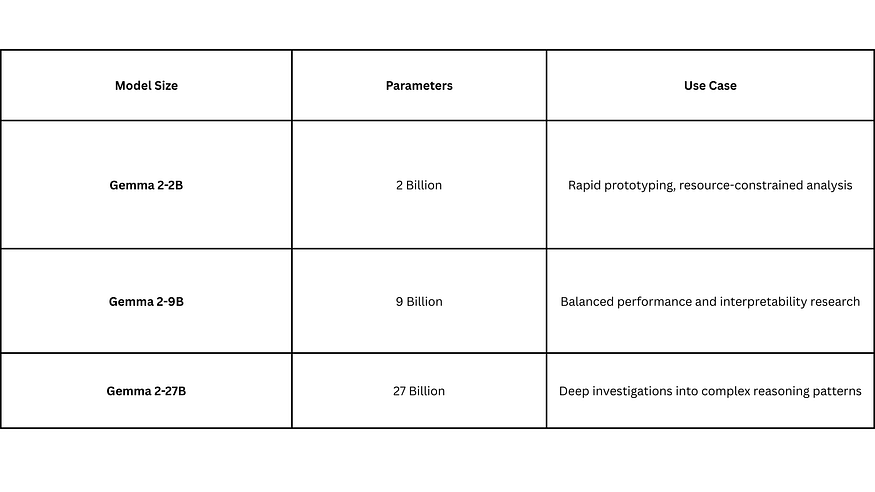
The toolkit provides pre-trained sparse autoencoders for Gemma 2 models across multiple scales:
Unlike earlier approaches relying on attention visualization, these autoencoders disentangle polysemantic representations where single neurons respond to multiple unrelated concepts. This enables practitioners to trace how specific concepts flow through the network during inference.
Practical Applications at Amlgo Labs
At Amlgo Labs, we’ve integrated interpretability techniques into our AI development workflow with tangible results:
Bias Detection & Mitigation: Using Gemma Scope’s feature decomposition, we identified activation patterns associated with demographic attributes. This enabled targeted debiasing at the representational level rather than crude output filtering.
Debugging Failure Modes: When models exhibit unexpected behaviour, we trace activation pathways to identify problematic intermediate representations. This has dramatically reduced iteration time for domain-specific adaptations.
Enhanced Red-Teaming: Understanding which features activate during problematic queries allows systematic exploration of safety boundaries and development of robust guardrails.
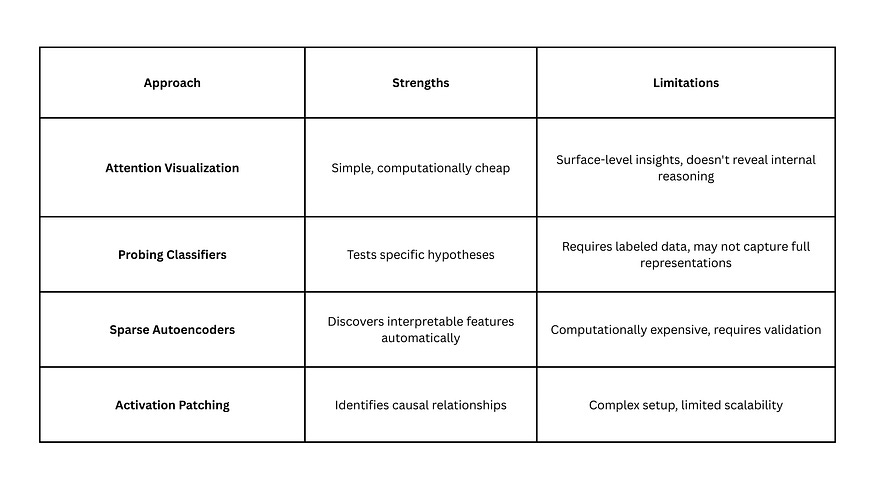
Key Interpretability Techniques Comparison
Gemma Scope 2’s sparse autoencoder approach strikes a balance between depth of insight and practical usability.
Implications for AI Safety
The release carries profound implications for AI safety research. Several key applications become tractable:
Adversarial Robustness: Move beyond black-box attacks to investigate which internal representations are vulnerable
Runtime Monitoring: Monitor specific high-risk features during deployment rather than relying solely on output filtering
Alignment Research: Study how values and objectives are actually represented within trained models
Researchers can now empirically test whether models develop deceptive representations, how safety fine-tuning affects internal reasoning, and whether architectural choices lead to more controllable systems.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite advances, significant challenges remain. Sparse autoencoders require careful validation to ensure that the extracted features are meaningful rather than artefacts. Computational costs limit access for smaller research groups. Most importantly, understanding representations doesn’t automatically solve alignment; interpretable features can still exhibit problematic patterns.
At Amlgo Labs, our research roadmap includes:
Developing automated interpretability analysis pipelines
Investigating cross-model feature correspondence
Exploring how interpretability enhances human-AI collaboration in high-stakes domains
Building Toward Transparent AI
Tools like Gemma Scope 2 represent meaningful progress toward AI systems that aren’t inscrutable black boxes. By democratizing interpretability infrastructure, we enable broader ecosystem participation in understanding and safeguarding these powerful systems.
For organisations like Amlgo Labs, which work at the intersection of capabilities and safety, interpretability is foundational. As language models advance in sophistication and deployment, our ability to understand and control their behaviour must advance in lockstep.
The open-source nature is crucial; AI safety cannot be the exclusive province of well-resourced labs. As we deploy increasingly capable systems across society, interpretability research offers a path toward development that’s not just more capable but more responsible.
At Amlgo Labs, we’re dedicated to advancing AI capabilities while prioritising safety, transparency, and alignment. We believe interpretability research is crucial to building AI systems that are powerful, trustworthy, and beneficial.


Comments
Post a Comment